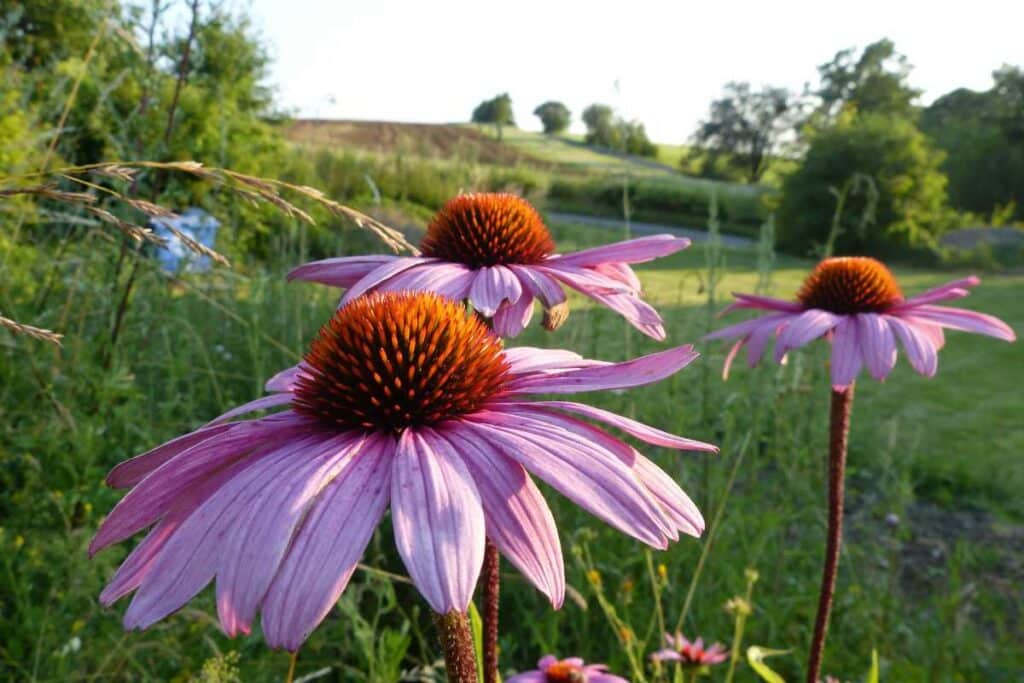
Echinacea, also known as Purple Coneflower, is a popular perennial plant found in many gardens. Prized for its vibrant colors and medicinal properties, echinacea is also drought-tolerant and deer-resistant, making it a reliable choice for gardeners.
However, the question of whether slugs eat echinacea is relevant for those looking to manage potential garden pests.
While echinacea may not be their first choice, slugs have been known to consume the plant, particularly during cool, wet conditions when other food sources may be scarce. The younger the plant the more at risk it will be from slugs.
Emerging echinacea shoots in early spring can be an attractive target for hungry slugs (Patient Gardener).
Although mature plants are less susceptible, gardeners need to be aware of how to protect their echinacea from potential damage caused by these slimy creatures.
Do Slugs Eat Echinacea?
Slugs can be a common garden nuisance, and many gardeners wonder if these pests are attracted to their echinacea plants.
Emerging echinacea shoots in early spring can be a delicious sight for hungry slugs when there’s not much else to eat. However, not all varieties of echinacea may be equally affected by slugs.
While slugs generally prefer to eat old, decaying material, they will munch on a variety of crop plants if their preferred food source is unavailable.
According to a discussion on the Gardener’s World Forum, some gardeners reported that neither slugs nor snails appeared to be devouring their echinacea plants.
While it’s clear that slugs may target echinacea under certain conditions, it’s also worth noting that there are many flowers that slugs and snails dislike eating. It may be beneficial for gardeners to plant a variety of slug-resistant flowers to deter these pests from wreaking havoc on their precious plants.
Echinacea Plant Characteristics
Echinacea, also known as coneflower, is a group of flowering plants native to North America. They are an attractive addition to gardens and are also known for their medicinal properties.
This section covers the characteristics of echinacea plants, including their types, growth habits, and ideal growing conditions.

Types of Echinacea
There are several species and varieties of echinacea plants, but three main species are commonly grown in gardens:
- Echinacea purpurea – The most well-known species, also called purple coneflower, features purple-pink flowers with a prominent central cone.
- Echinacea angustifolia – Also known as narrow-leaved coneflower, it has narrower leaves and slightly smaller flowers compared to E. purpurea.
- Echinacea pallida – Pale purple coneflower has pale pink petals that droop downward, creating a distinctive appearance.
Growth Habit and Conditions
Echinacea plants are known for their hardiness and adaptability, making them suitable for a range of garden settings.
They typically grow to a height of 2 to 4 feet and spread up to 2 feet wide. The plants form a clump of basal leaves and send up tall, sturdy stems topped with large, showy flowers.
Blooms are most abundant in the summer months but may persist into autumn.
Ideal growing conditions for echinacea plants include:
| Aspect | Preference |
|---|---|
| Soil | Well-drained, loamy soil; can tolerate clay and sandy soils |
| Light | Full sun to light shade |
| Water | Moderate water needs; drought-tolerant once established |
| Temperature | Can tolerate temperatures down to -20°F; grows well in USDA zones 3 to 9 |
Although echinacea plants are relatively low-maintenance, they can be susceptible to damage from slugs, particularly during the early stages of growth.
Proper care, such as reducing excess moisture and considering slug-resistant plants in the garden plan, can minimize damage and ensure healthy echinacea plants.
Section 4: Slugs and Their Diet
Common Types of Slugs
There are several types of slugs that can be found in gardens and other outdoor spaces. Some of the most common species include:
- Grey Field Slug (Deroceras reticulatum)
- Garden Slug (Arion hortensis)
- Black Slug (Arion ater)
- Large Black Slug (Limax cinereoniger)
Feeding Preferences and Habits
Slugs are nocturnal creatures that are primarily herbivores, feeding on various types of plant material.
They generally prefer to eat old decaying material, making them important decomposing organisms. However, if decaying material is not available, they will feed on a wide range of plants, including certain crops and ornamental garden plants.
Some plants are more attractive to slugs than others, such as larkspurs, sunflowers, hostas, dahlias, and zinnias (SlugHelp).
Concerning echinacea, emerging shoots in early spring may tempt hungry slugs due to a lack of other food sources (Patient Gardener). However, some gardeners have not experienced issues with slugs eating their echinacea plants (Gardeners’ World Forum).
Preventing Slugs from Eating Echinacea
Echinacea plants can be a target for slugs, especially when they are young and tender. To protect your echinacea plants from slugs, you can implement a variety of preventive measures, including natural deterrents, chemical deterrents, barriers, and traps.
Natural Deterrents
Natural deterrents can help to repel slugs from your echinacea plants without using chemicals. Some common natural methods include:
- Introducing beneficial predators, like frogs or ground beetles, to the garden, as they can help to control slug populations.
- Placing crushed eggshells or coarse sand around the base of echinacea plants to create a scratchy surface that slugs will not like to cross.
- Using plants with strong scents, like marigolds or lavender, as a border around the echinacea to create a natural barrier that slugs may avoid.
Chemical Deterrents
If natural deterrents are not effective enough, you can resort to chemical deterrents. Keep in mind that using chemicals may have an environmental impact. A few chemical options are:
- Applying iron phosphate baits around the echinacea plants, which can help to control slug populations. Make sure to follow label instructions for proper application.
- Using diatomaceous earth as a dry barrier around the plants. This substance has sharp edges that can injure slugs when they try to cross it, deterring them from reaching your echinacea.
Garden Safe Slug Bait

Monterey Slug Killer
- Kills earwigs, cutworms, sowbugs, pillbugs, slugs, snails
- For use around vegetables, fruit trees, citrus, berries, ornamentals, shrubs, flowers, trees, lawns, gardens and in greenhouses (non-commercial)
- Treats 2000 SQFT
- Pet Safe
- Quick and easy to apply
- Contains spinosad – derived from a naturally-occurring soil dwelling
Barriers and Traps
Another approach to preventing slugs from eating echinacea is by using physical barriers and traps. Some methods you can use are:
- Creating a copper barrier around the echinacea plants by using copper tape or mesh. Slugs will receive a small electrical shock when they come into contact with the copper, preventing them from crossing.
- Setting up traps, such as beer traps, where slugs are attracted to the beer and drown in it. Place the traps in the evening and empty them in the morning. Replace the beer every few days to keep the trap effective.
By employing these protective measures, you can help to keep your echinacea plants healthy and free from slug damage.
What Flowers Do Not Attract Slugs?
Slugs are notorious for munching on a variety of plants, but some flowers naturally repel these pesky creatures.
These plants have either tough or hairy foliage, emit strong scents, or contain compounds that slugs do not find appetizing.
One such example of slug-resistant flowers is aquilegia, which is mentioned on the BBC Gardeners World Magazine list of plants slugs do not like to eat. Another option is turning to ferns, which, according to The Spruce, are also unappealing to slugs due to their texture and lack of flowers.
For an easy-to-read selection of plants that slugs typically avoid, consider the following list:
- Aquilegia
- Ferns
- Sedum
- Geraniums
- Epimedium
- Lavender
- Rosemary
- Foxgloves
- Japanese anemones
- Iris
By incorporating these slug-resistant flowers into your garden, you can help protect your other plants, including echinacea, from potential slug damage.
Remember to keep your garden clean and implement other slug control measures to further reduce the chances of attracting these pests.
Conclusion
Slugs are known to feed on a variety of plants, including echinacea. While echinacea may not be their preferred plant, these pests can still cause damage, especially to young and vulnerable plants, as mentioned on Patient Gardener and Smart Gardener.
Echinacea, however, can become more resistant to slugs as it grows and becomes stronger. Established echinacea plants may still be impacted by slugs, but the damage is often less severe, as stated by Patient Gardener.
Slug control is crucial for the survival and health of echinacea plants. There are various natural methods to keep slugs at bay, as mentioned on David Domoney’s blog.
Employing these methods can help protect your echinacea plants and allow them to thrive in your garden.