Most people believe that aquaponics is a complex system of rearing fish.
The truth is, it’s not complicated once you understand how it works and how to maintain it. Aquaponics is a symbiotic system that combines aquaculture with hydroponics.
The aquatic animals rely on the plants for food, while the plants depend on the fish excretion for nutrients. The fish play a significant role in the aquaponic system.
Therefore, the overall health of the fish majorly depends on maintaining the optimum conditions for the fish to thrive.
Some things to consider include:
- Feeding
- Water pH
- System size
- Water temperature
- Nutrition
- Light and
- Hygiene
Caring for Fish in an Aquaponic System
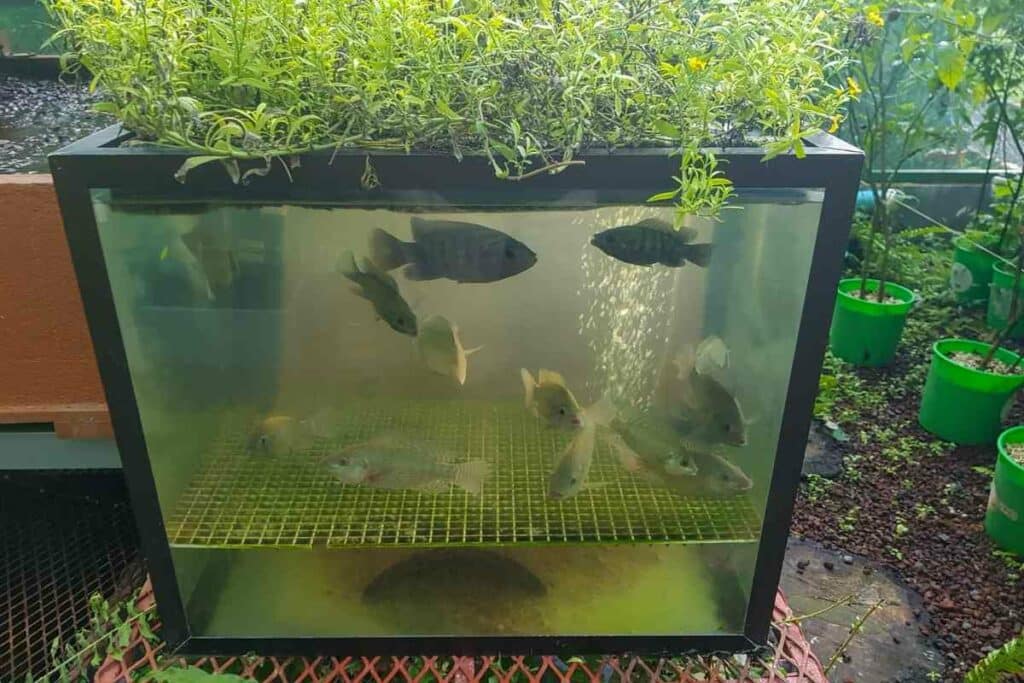

Below is a comprehensive guide on aquaponics fish care to make your system a success.
Proper Fish Species
To ensure your aquaponic system lasts long, you need to have ideal fish species.
The most common fish recommended for aquaponics are tilapia, carp, catfish, trout cod, salmon, and bass. Having suitable fish species allows you to maintain the proper aquaponic conditions for their survival.
Additionally, the compatibility of all your fish is essential. For example, an aggressive species will cause stress to other fish and affect their overall health.
So understand compatibility among fish species and monitor fish behavior and habits such as unusual swimming patterns and positioning.
Water Temperature
Fish will not thrive if they are too cold or too hot because they do not regulate their body temperature as mammals do.
Also, different fish species need different temperature levels. Some are cold-water species, while others are warm-water species.
Coldwater fishes thrive in temperatures of at least 57°F, and warm water species require water temperatures of at most 86°F. Fast temperature changes can also cause stress in fish and lead to bad health or death.
Don’t Forget: You need to adjust your water temperatures accordingly to ensure you provide an ideal environment for your fish.
Water pH Levels
Check the water pH weekly and maintain the level at a neutral range of 6.8 to 7.0.
You can lower the pH by adding the pH down liquid or use a pH up solution to raise it. These are food-grade solutions that stabilize the pH without harming your fish.
Make small increments to the fish tank water until you achieve the proper pH.
Plant Health
The plants in the aquaponic system need to be in good health for the fish to thrive.
Inspect the plants for pests and diseases and treat them accordingly. Ensure the plants are well spaced and add fans in the room to regulate room temperature.
Avoid plant overgrowth by harvesting mature crops. Plants also have different requirements; therefore, you need to create conditions suitable and adaptable to your plant’s specifications.
Fish Nutrition
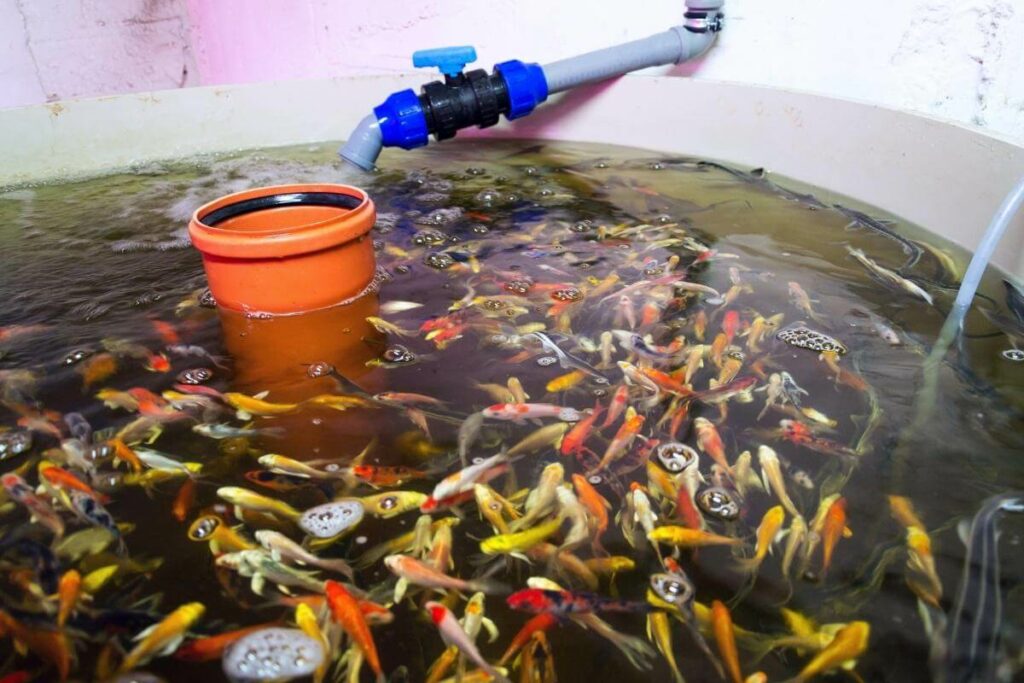

Strictly, feed the fish 2-3 times per day. Do not overfeed them.
The rule of thumb is to feed your fish with only what they can eat within five minutes. Remove any extra food from the tank as excess solid waste will reduce the water quality.
The food you feed them also has to provide adequate and quality nutrition. Commercial fish feeds contain the right amount of protein, carbohydrate, fats, and mineral requirements depending on the type of fish.
Quick Tip: Avoid fish meal-based feeds as they are not sustainable.
Aeration
Oxygen in the fish tank reduces when water temperature increases which puts the fish under stress.
Your fish will die within 30 minutes if deprived of oxygen. Clean the air stones by soaking them in diluted hydrogen peroxide solution and scrubbing them with a brush to remove bio slime.
Check the aerator regularly to ensure it’s working correctly. If you live in a warmer area, install an additional aerator.
Finally, ensure you have a power backup standby for the aerators and pumps.
Water Quality
Carefully monitor your water quality frequently to ensure the fish remain healthy.
Add water or do partial water changes with temperate, dechlorinated water to remove any sediments at the bottom of the tank.
Too many solids in the fish tank will lead to heterotrophic bacteria overgrowth, which breaks down the solids and competes with the nitrifying bacteria for space and oxygen.
This will result in denitrification reducing the nitrates needed by plants.
Ammonia and Nitrate Levels
Check the nitrate and ammonia levels in your aquaponic fish tank once a month.
The nitrate levels shouldn’t exceed 150ppm, while ammonia levels should be less or equal to 0.5ppm. Poor hygiene, overfeeding the fish, and overstocking will increase nitrate levels.
High concentrations of nitrates will prevent your plants from absorbing nitrogen released by the nitrifying bacteria.
Here’s how to reduce nitrate levels in your system:
- Change 25-50% of the water
- Reduce feeding
- Remove excess fish food,
- Clean the tank
- Increase aeration.
Hygiene
You must maintain the proper hygiene of your fish tank to reduce the risk of plant and fish diseases.
Here’re 3 basic steps:
- Clean the beds when changing the crops. Flush out the water and then refill it with dechlorinated water.
- Check the plumbing system and get rid of any clogging.
- Clogged pipes have low pressure, which reduces adequate water flow through your system.
Don’t Forget: This is also the time to replace any damaged parts.
Promote Nitrifying Bacteria

Fish releases waste into the water as ammonia, and bacteria consume fish waste to produce nitrite.
Nitrites are toxic to fish, but nitrifying bacteria convert nitrites to nitrates. Nitrates are the primary source of plant nutrition.
The nitrifying bacteria perform slower in temperatures below 60°F and above 80°F. This causes a decline in ammonia and nitrate conversion, increasing waste in the fish tank.
To fix it, you need to deep-clean the fish tank or buy some nitrifying bacteria to prevent nitrite poisoning of the fish.
Prevent Growth of Algae
Stop algae growth in the fish tank as they increase competition for nutrients and oxygen.
Cover your fish and sump tanks and keep them away from direct sunlight.
Pest Control
Check for aphids, whiteflies, and other pests around the stems of the crops at least weekly.
Combine white vinegar and water to make a homemade pesticide solution and spray around the crops.
Do not use pesticide products with neem oil or pyrethrum; although they are organic, they are toxic to fish.
Final Thoughts
You must take proper care of your fish to get the most out of your aquaponics system.
There is a delicate balance of temperature, pH, aeration, water quality, and sunlight in the fish tank to ensure healthy fish.
Follow the tips shared, and you’ll create the most suitable environment for your fish to thrive. You can start small with a mini aquaponic ecosystem like this one.