The philodendron family of plants includes a wide range of exotic climbing and shrubby houseplants known for their luxuriant foliage and colorful stems.
Their diversity and often strange fenestrated leaves make them a feast for the eyes, and despite hailing from South America, these plants are reasonably adaptive, making them great houseplants.
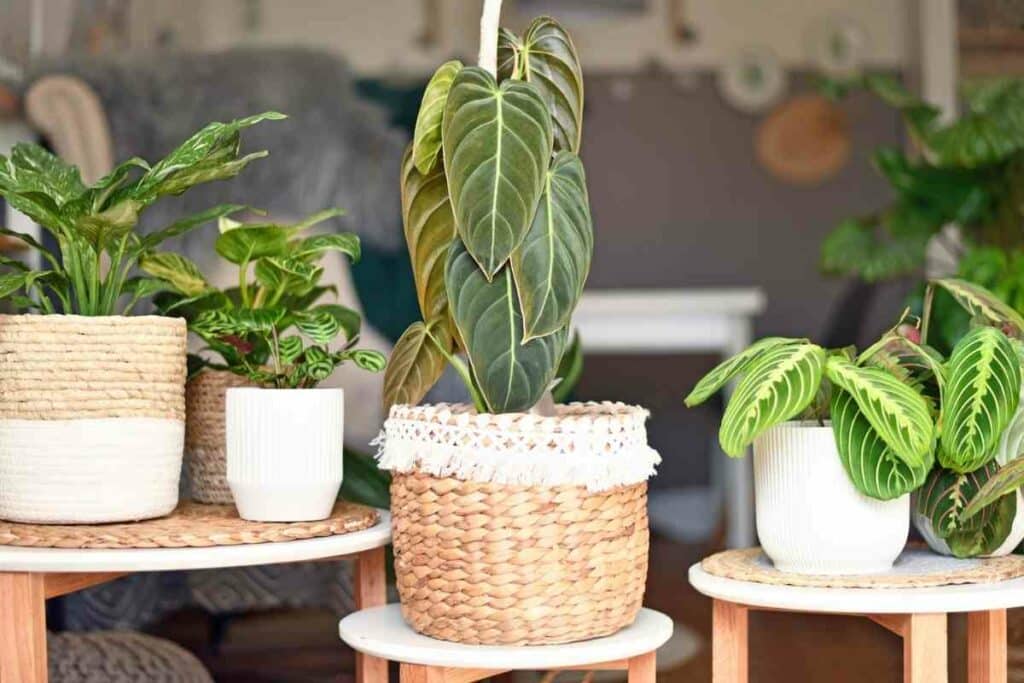

We’ve gathered beautiful images of 7 popular philodendron types for you to enjoy.
About Philodendrons
Philodendrons are a huge genus of over 450 flowering plants that mostly come from the Araceae family.
They come from South America and certainly have a rainforest feel with their vine-like growth and shrubs, its bright stems, and large glossy leaves.
Their name is appropriate as it comes from the Greek words ‘Philo’ meaning love and ‘Dendron’, meaning tree.
Since their discovery by Europeans in the late 17th century, they have gained worldwide popularity as ornamental plants.
Common features of philodendrons
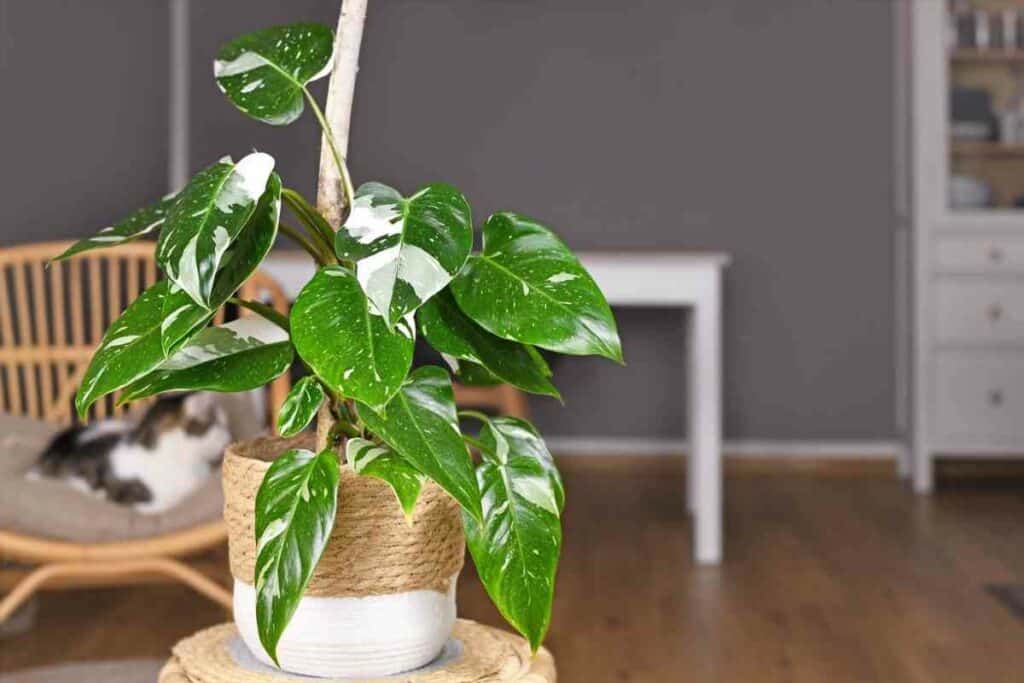

Some philodendrons look pretty strange, but some common features of philodendrons include:
Broad, glossy leaves
The leaves are the showpiece of the philodendron.
They’re broad, glossy and often variegated, lobed, or frankly fenestrated. The variety of large quirky leaves makes philodendron plants highly collectible and a beautiful display.
Spathe and spadix
Philodendrons do flower, producing a cup-like leaf called a spathe and a flower spike called a spadix.
They attract beetles to spread their pollen and some of their fruit is edible.
Aerial and subterranean roots
As you grow your philodendron, you may notice that it develops significant aerial roots that grow from nodes and internodes.
In some climbing varieties, they can be trained to wrap around a moss pole.
7 Philodendron Types
1. Philodendron ‘Xanadu’
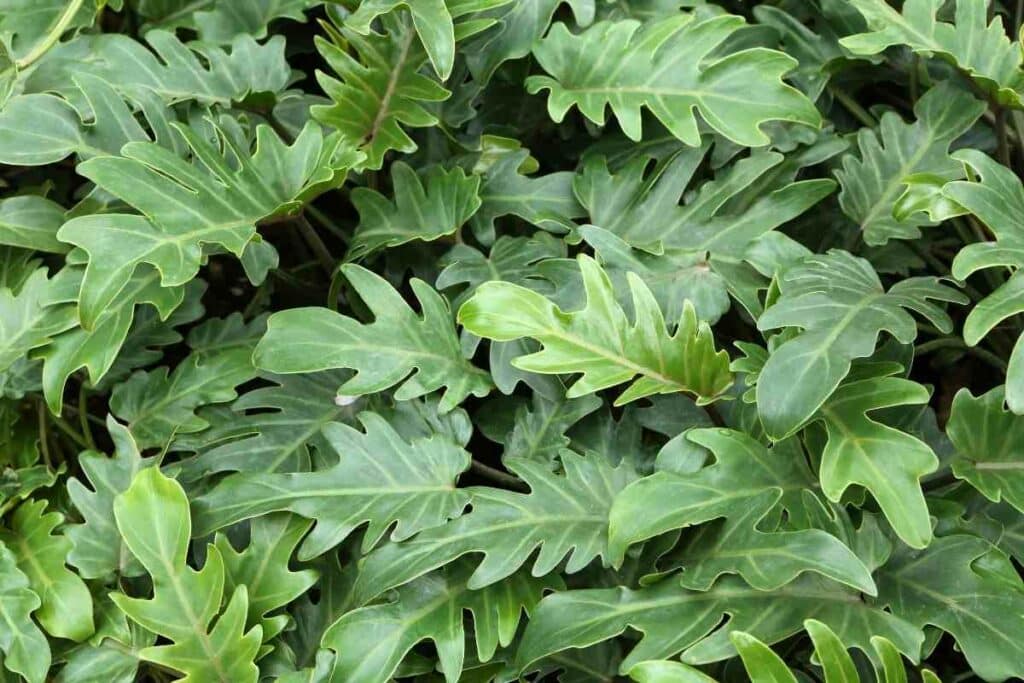

Variety name: Philodendron ‘Xanadu’
Also known as: Philodendron bipinnatifidum, Winterbourn, or ‘cut-leaf’ philodendron
Description: The Xanadu philodendron is a popular house plant that has shiny dark green leaves on long thin stems that are beautifully lobed with up to 20 lobes per leaf. This philodendron is upright but grows wide, forming clumps with its leaves growing out of a thick and woody stem. It may also form aerial roots.
Maximum height and spread: P. Xanadu can achieve a maximum height of 1.5 meters and a spread of up to 2.5 meters. It takes up to 20 years to achieve its maximum size.
Flowering: When kept as an indoor houseplant, P. Xanadu rarely blooms. If it flowers, it produces dark red spathes.
Care: Loamy, well-draining soil, and high humidity P. Xanadu attract sap-sucking pests.
Toxicity: The Xanadu philodendron is poisonous. Keep it away from pets and children.
2. Philodendron ‘Erubescens’
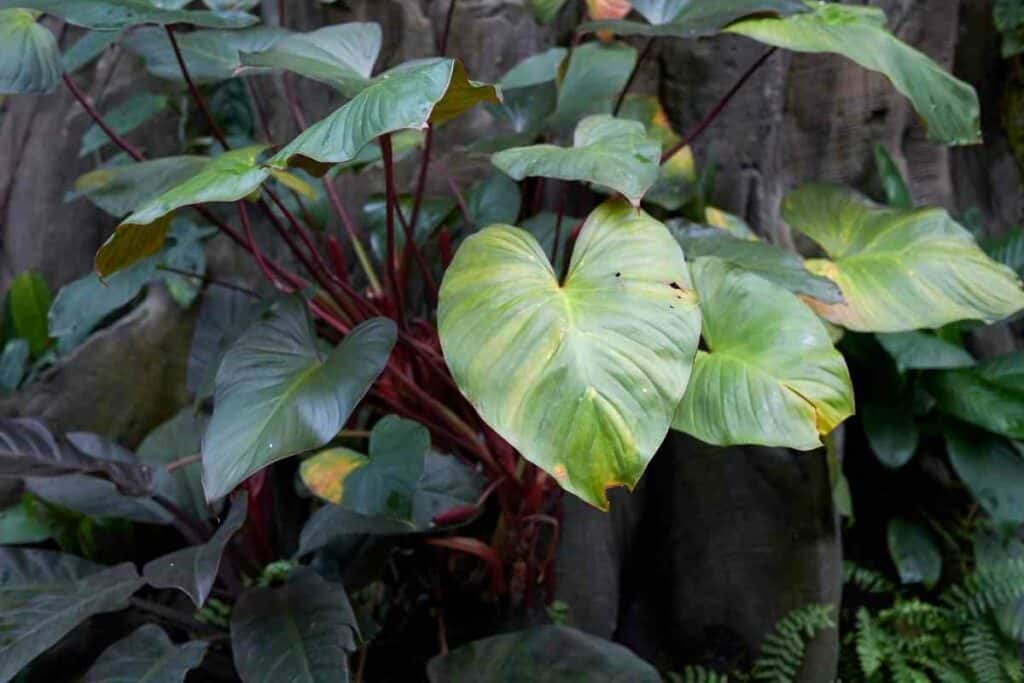

Variety name: Philodendron erubescens
Also known as: blushing philodendron or red-leaf philodendron.
Description: This gorgeous philodendron is an avid climber and can achieve heights of 3 to 6 meters if you have a moss pole that is long enough. P. erubescens comes from Colombia and has given rise to a variety of hybrids, some of which are shared below.
Its vivid red stems are a notable feature, along with its aerial roots that you can train. The heart-shaped leaves are big and broad and can be up to 16 inches (40 centimeters) in length. In in-direct light, the leaves of certain varieties become beautifully variegated.
Maximum height and spread: P. erubescens can climb to heights of 10 to 20 feet (3 to 6 meters)
Flowering: Summer and autumn flowering of large (up to 6 inches / 15 centimeters) deep red spathes that are fragrant.
Care: Position this philodendron away from direct, bright sunlight as it causes discoloration of the leaves. Plant in a loamy, nutrient-rich soil that drains quickly and consider repotting every two years. P. erubescens requires moderate watering with less in winter. Feed P. erubescens during its growing season from April to October.
Toxicity: All parts of Philodendron erubescens are poisonous. Keep it away from pets and children.
3. Monstera Philodendron
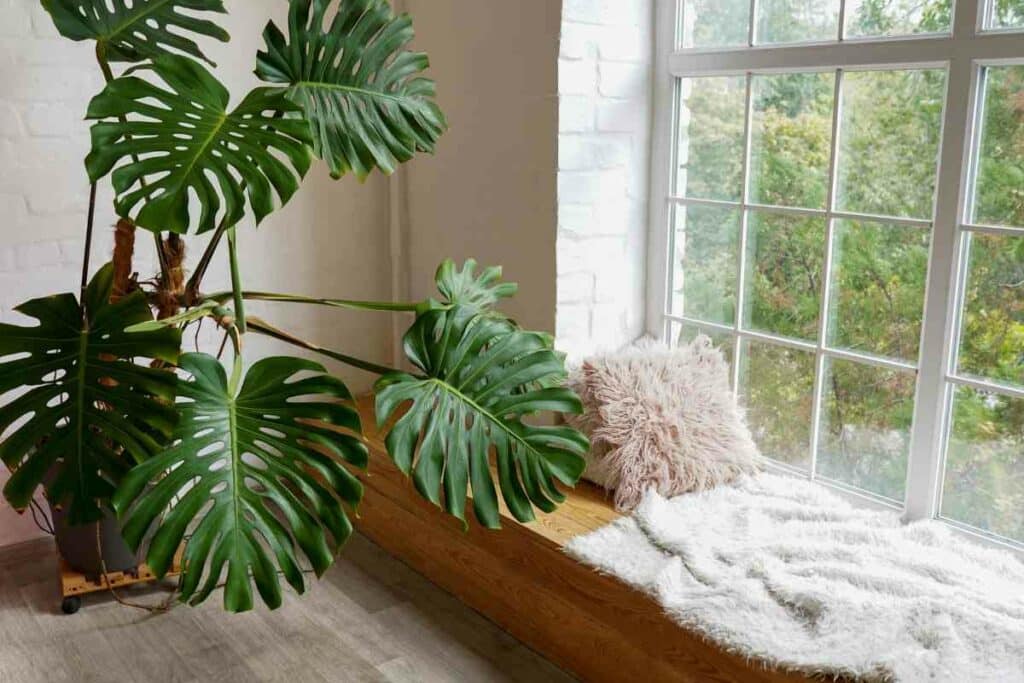

Variety name: Monstera Philodendron
Also known as: Monstera deliciosa, Swiss cheese plant, window leaf, or split-leaf philodendron
Description: This quirky philodendron brings drama with its unusual leaves with natural holes in a variety of patterns depending on the cultivar. The strange heart-shaped leaves of this South American native have earned it the name ‘monstrous’ (monstera) and Swiss cheese. The holes and deep lobes develop over time as the leaf grows.
Its striking appearance makes it popular as a houseplant, but in the wild, it is a trailing vine that can achieve a maximum height of 70 feet or more. The leaves grow off a heavy, scarred stem which may also have aerial roots.
Maximum height and spread: With plenty of TLC a split-leaf philodendron houseplant can grow up to 15 feet tall (4.5 meters) and 8 feet (2.4 meters) wide.
Flowering: Monstera philodendron rarely flowers. When it does, it produces a fleshy flower spike with small flowers, enclosed in a spathe. It may also produce an edible fruit that tastes like a combination of pineapple and banana!
Care: This plant appreciates bright light in the summer and as much direct sun as possible in the winter. It also needs warmth, humidity, and robust support to thrive. Plant in a rich but well-draining soil and fertilize during its growing season.
Toxicity: All parts of the Monstera Philodendron apart from its fruit are poisonous (oxalic acid). Keep it away from pets and children.
4. Philodendron ‘Shangri-La’
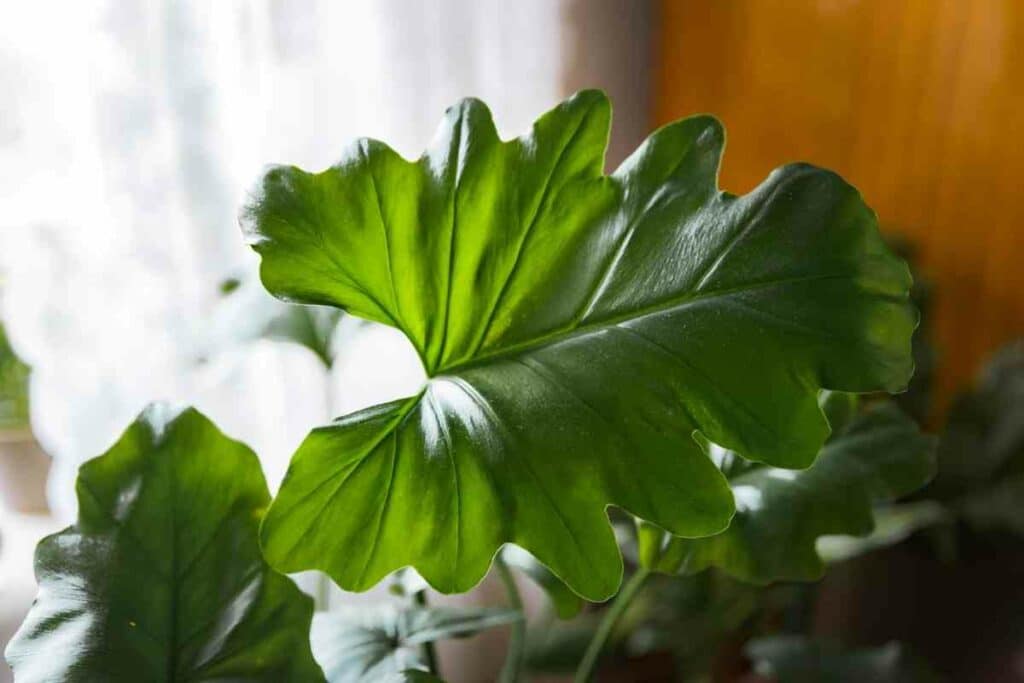

Variety name: Philodendron ‘Shangri-La’
Also known as: Philodendron bipinnatifidum, horsehead philodendron, Philodendron selloum, split-leaf philodendron, lacy tree philodendron
Description: Philodendron lovers will delight in this busy split-leaf philodendron that makes a really bushy indoor or outdoor plant. Its foliage is its centerpiece; numerous sturdy stems terminating in large deep-green leaves with lime-green veins and a jagged ‘split-leaf edge’ that deepens as the leave grows!
Shangri-La is a mounding philodendron with new stems and leaves growing from its center rather than climbing as a vine. This makes it an ideal choice for a houseplant as it does not require careful support.
Maximum height and spread: This is a great choice for a compact, but beautiful display. P. Shangri-La usually has a maximum height and spread of 20 inches (50 centimeters) in both directions.
Flowering: P. Shangri-La produces a spathe with small male and female flowers housed within.
Care: P. Shangri-La loves bright but indirect light and plenty of warmth. Direct sunlight can burn the leaves. Plant in rich, well-draining soil, watering only when the top two inches of soil dry out. Feed monthly.
Toxicity: All parts of Philodendron ‘Shangri-La’ contain oxalate crystals, making it poisonous.
5. Philodendron ‘Rojo Congo’
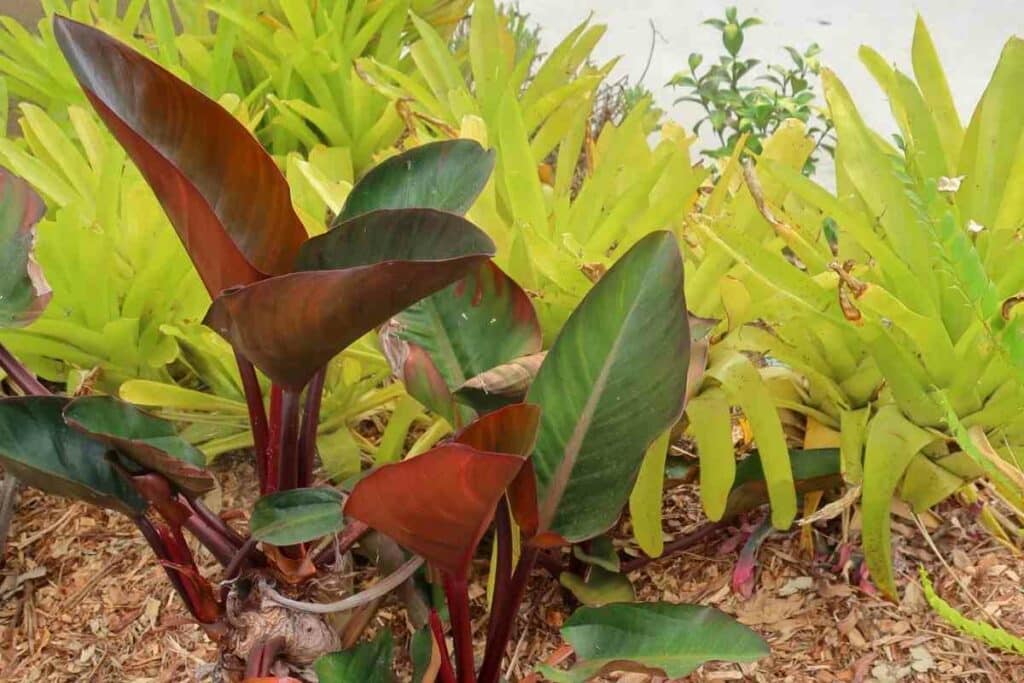

Variety name: Philodendron ‘Rojo Congo’
Also known as Philodendron tatei, Philodendron Rojo Congo, Rojo Philodendron, Congo Rojo, Red Congo.
Description: As the name suggests, this philodendron is all about red. Its striking red stalks give rise to copper-red leaves that mature to a deep glossy red and deep green. P. Rojo Congo, like other philodendrons, hails from South America. Their compact growth makes them a great choice for a smart houseplant with plenty of character.
Maximum height and spread: Rojo Congo do not climb and is a ‘self-heading’ plant that typically reaches a maximum height of 2 feet (61 centimeters) and a spread of 2 ½ feet (76 centimeters).
Flowering: P. Rojo Congo can produce a spathe, but flowering in houseplants is rare.
Care: As a slow grower, maintenance is easy but adequate sunlight is a must. Make sure that your Rojo Congo enjoys at least 3 to 4 hours of indirect bright light daily. Direct sunlight will burn its leaves, but low light will cause this philodendron to rot. Like other philodendrons a rich, but fast-draining soil is key. Avoid overwatering, the top two inches of soil should be dry before you water this plant again. Fertilize monthly during the growing season.
Toxicity: All parts of Philodendron Rojo Congo contain are poisonous.
6. Philodendron Squamiferum
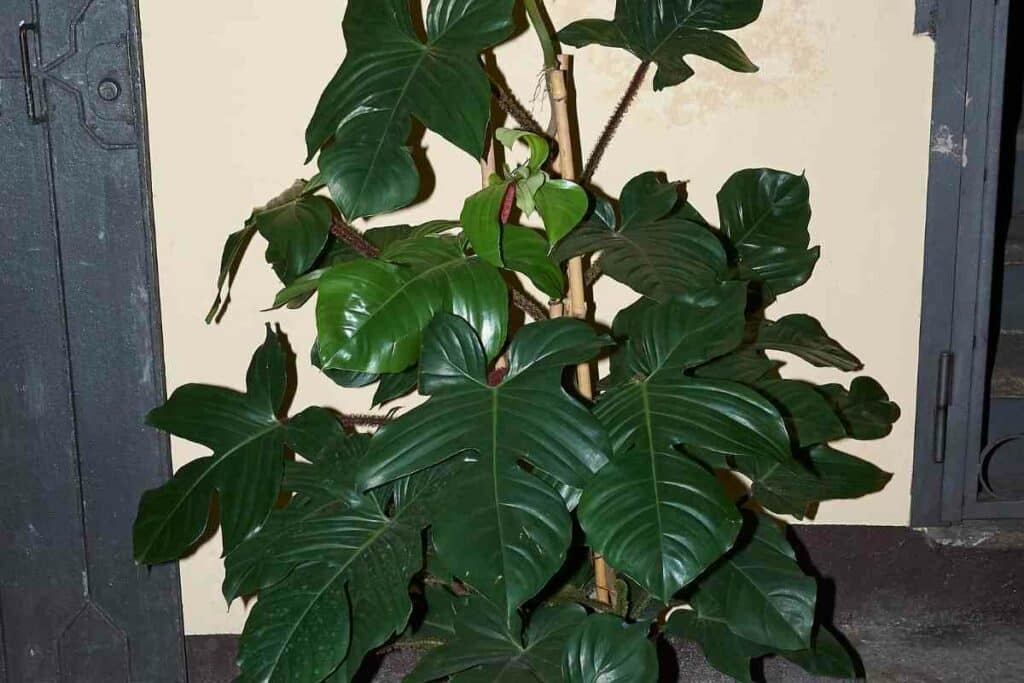

Variety name: Philodendron squamiferum
Also known as: Philodendron tatei, Hairy Philodendron, Red Bristle Philodendron, The Hairy Philodendron, Philodendron red bristle
Description: This popular philodendron is a beautiful climbing plant with five-lobed dark green leaves that is native to Brazil, Suriname, and French Guiana. Its common name is due to it having scaly, bristly red stalks. The leaves of Philodendron red bristle start as whole, elongated leaves and become lobed as they mature. The mature, dark green leaves are up to 10 inches (25.4 centimeters) long and have two posterior lobes, two middle lobes, and a rhomboidal terminal lobe.
Maximum height and spread: As a fast-growing climber, the Hairy philodendron can reach heights of up to 8 feet (2.5 meters).
Flowering: Hairy philodendron produces spathes during late spring and summer. They contain small white flowers that give rise to pink seeded berries.
Care: As a tropical plant, P. Red Bristle thrives in bright, warm, humid conditions. Avoid placing this plant in direct sunlight and water it only when the first two inches of soil dries out. Feed it during the spring and summer months until early fall, or monthly if grown indoors.
Toxicity: Like other philodendrons, Philodendron Red Bristle contains oxalic acid crystals that can cause skin and digestive system irritation.
7. Philodendron Mandianum
Variety name: Philodendron Mandianum
Description: This classic philodendron is a hybrid of P. Erubescens and makes a stylish addition to any home! It has beautiful deep red stems and petioles, topped off with glossy dark green leaves. It may also develop aerial roots as it grows.
Maximum height and spread: This is a slow-growing and self-heading philodendron, so it won’t climb or take over your home. Its nodes are close together on the central stem, so it grows bushy.
Flowering: P. Mandaianum flowers by producing a spathe, but this is less frequent in houseplants.
Care: Treat your P. Mandaianum to a fast-draining potting mix and water lightly. This plant is very adaptive so you can get away with placing it in a location with low light.
Toxicity: Philodendron Mandaianum contains oxalic acid crystals and is poisonous to children and pets.
Rounding Up
These seven gorgeous philodendron varieties are a feast for the eyes and make a beautiful addition to any home, garden, or glasshouse.
If you can keep them warm, these rare and unusual exotic houseplants should thrive and we’re sure you’ll search for other varieties to add to your collection.