Are you fighting the good fight against tall garden weeds in your garden?
Here is some help in identifying and managing 11 tall garden weeds that can cause enormous problems for gardeners, landscapers, horticulturists, and farmers.
11 Tall Garden Weeds
It is not difficult to miss these tall garden weeds.
Every single species profiled achieves growth of over 1.5 metres in height in a single summer and are very efficient at spreading prolifically.
Have a look at these mugshots and our advice on the best methods of eradication.
1. Paulownia Tomentosa
Also Known As: Paulownia Tree, Foxglove-Tree, Princess Tree, Empress Tree
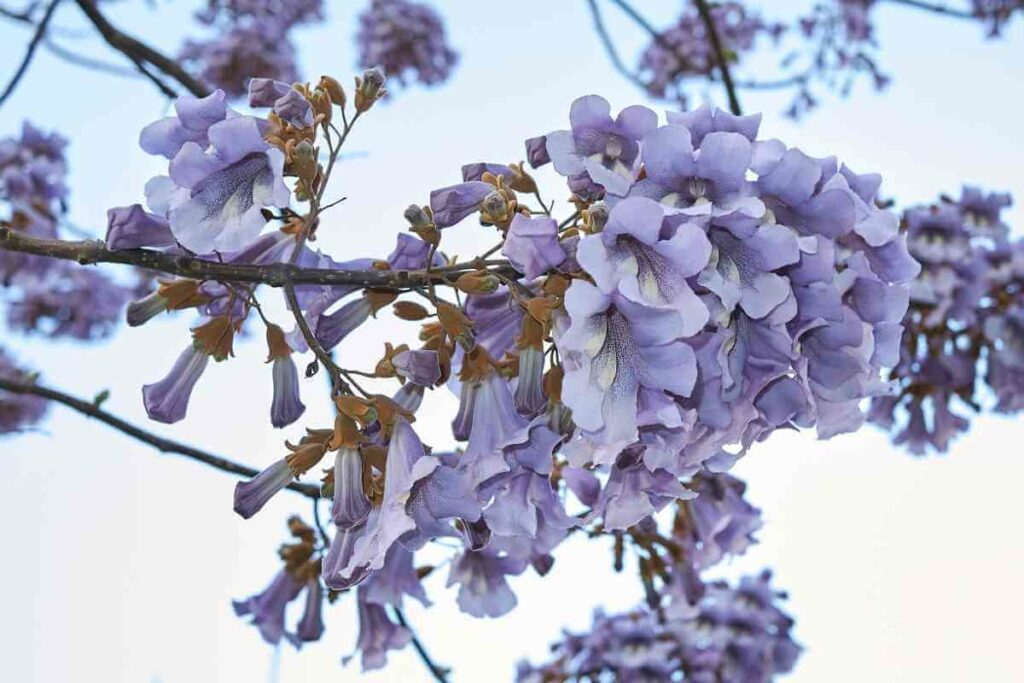

Distribution: Native to China and the Korean peninsula, invasive in North America, introduced to Europe and South Africa.
Description
You may be incredulous at the thought of a full, blown tree being a garden weed, but this deciduous hardwood is known for its fast growth and invasiveness which has been wreaking havoc across North America!
It is hard to imagine a taller garden weed with its young growth can achieve a growth rate of over 2.5 metres per season.
The young growth has whorls of heart-shaped or multi-lobed leaves.
It produces a large foxglove-like flower which yields fruit and seed that are widely disseminated by wind and water.
Eradication Strategies:
- Uprooting saplings
- Cutting into the tree
- Spraying insecticide into the slits
2. Pokeweed
Also Known As: Phytolacca Americana, American Pokeweed, Dragonberries, Poke Sallet, Inkberry, Poke Salad
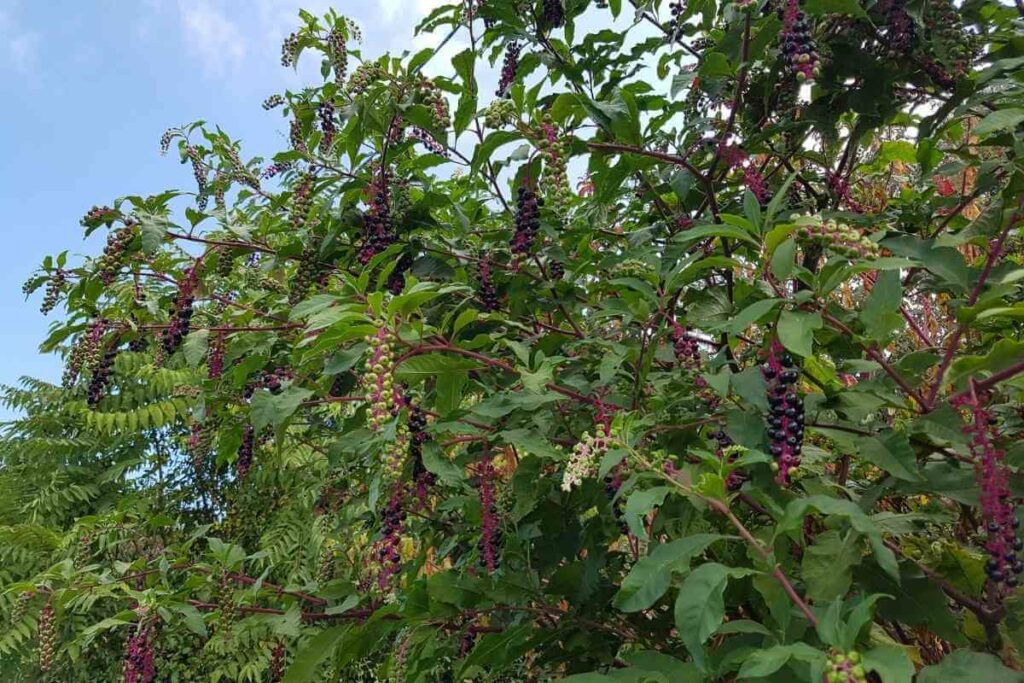

Distribution: Native to eastern North America, introduced to Europe and Asia.
Description
This is a nasty poisonous plant that has a long history of killing people who ingest its roots, leaves and berries.
Pokeweed is an extremely tall herbaceous plant that spreads and achieves heights of up to 2.5 meters in a single summer.
As it matures, it gets more and more toxic.
Its bright green foliage purplish stems and large black berries make it hard to avoid and a risk to youngsters who may want to taste the berries.
Eradication strategies:
- Insecticides
- Digging up the taproot
3. Rhododendron
Also Known As: Rhododendron Ponticum, Common Rhododendron, Pontic Rhododendron
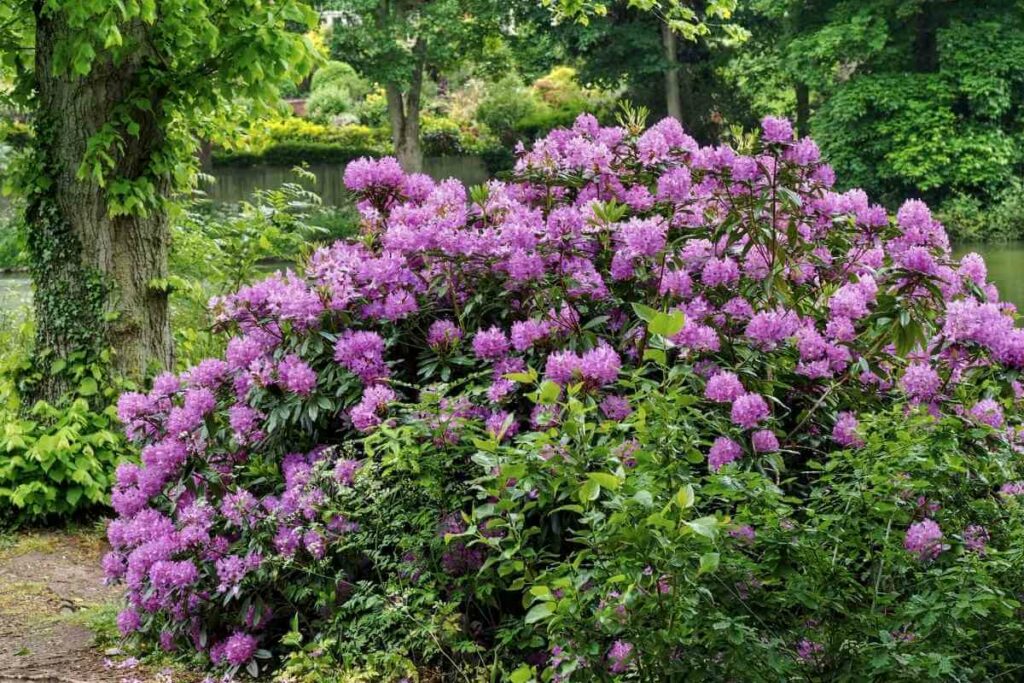

Distribution: Native to the Iberian peninsula and the Caucasus, invasive in Western Europe and New Zealand.
Description
Rhododendron has caused problems for British horticulturalists since its deliberate introduction in the 18th century.
This dense, suckering shrub is a prolific grower and highly invasive. It is evergreen and produces purple flowers which give rise to fruit with many seeds.
It easily achieves heights of up to 5 meters with similar aggressive horizontal spread.
Rhododendron is also toxic, with even honey produced from the pollen of its flowers capable of poisoning.
Eradication strategies:
- Stem injection control
- Digging up the shrubs after treatment with insecticide
4. Ricinus
Also Known As: Ricinus Communis, Castor Bean
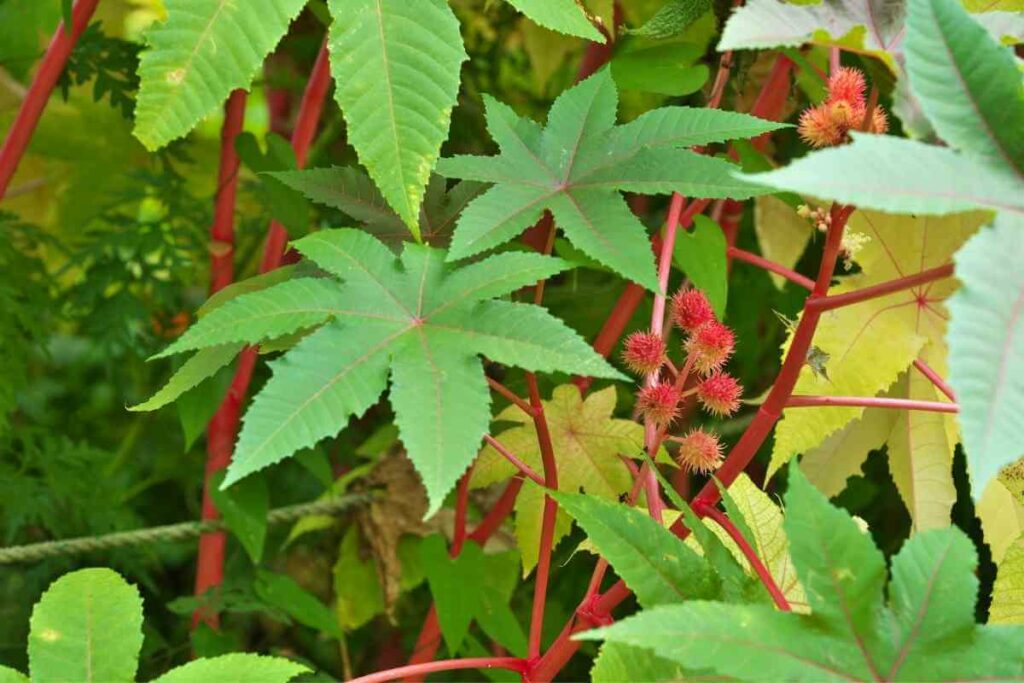

Distribution: Native to the Mediterranean, Africa and Asia, invasive in the southwestern US
Description
This roving perennial flowering plant is known for its beans (seeds) and the oil that is produced from them.
It usually grows as a shrub but can achieve heights of 10 feet or more. Its spread is opportunistic, with it taking over wasteland, fields and growing by roadsides.
The foliage and seeds are toxic, making it problematic if the plant grows among crops and the seeds inadvertently enter animal feed.
Eradication strategies:
- Mechanical methods like cutting, pulling, disking
- Chemical control
5. Japanese Knotweed
Also Known As: Donkey Rhubarb, Polygonum Cuspidatum, Fallopia Japonica, Reynoutria Japonica and Asian Knotweed
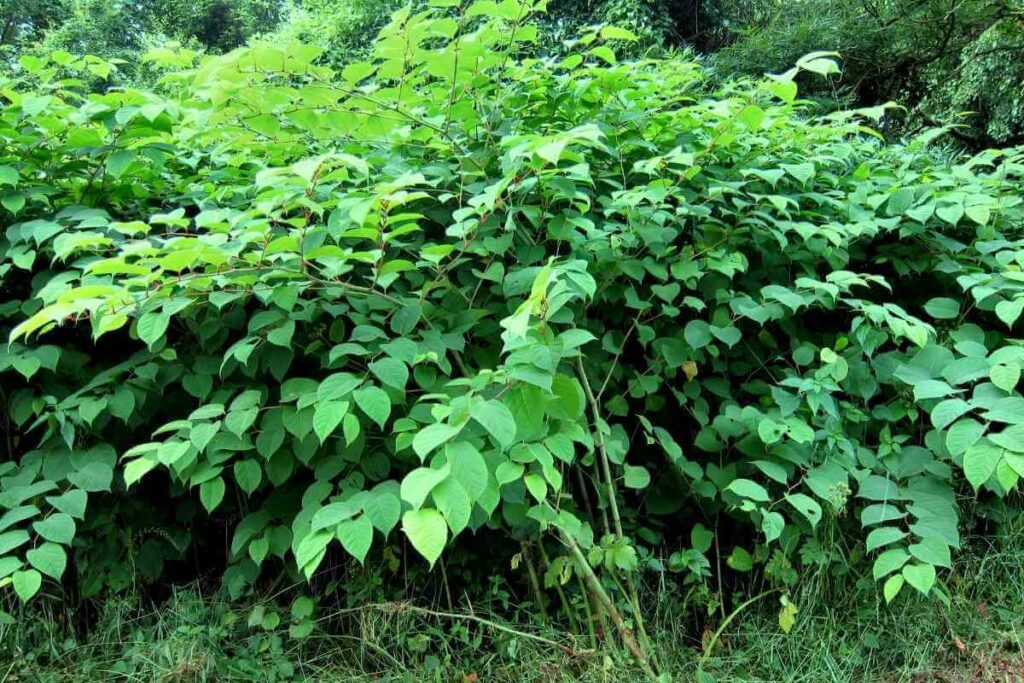

Distribution: Native to East Asia including China, Japan and Korea. Invasive in the US and western Europe.
Description
Japanese knotweed is a hollow-stemmed plant that produces raised nodes and can reach heights of 3 to 4 metres in each growing season.
It has broad oval leaves and produces racemes of small creamy flowers. It is highly adaptable and has an extensive root network meaning that it will repeatedly sprout if cut down.
Interestingly, Japanese knotweed that has not been treated or grown on contaminated land is edible.
Japanese knotweed specimens must be disposed of at licensed landfill sites or dried and burned.
Eradication strategies:
- Repeated applications of glyphosate
- Digging up
6. Wild Lettuce
Also Known As: Lactuca Virosa, Rakuten-Karyamu-So, Laitue Vireus, Tall Lettuce, Great Lettuce, Bitter Lettuce or Opium Lettuce
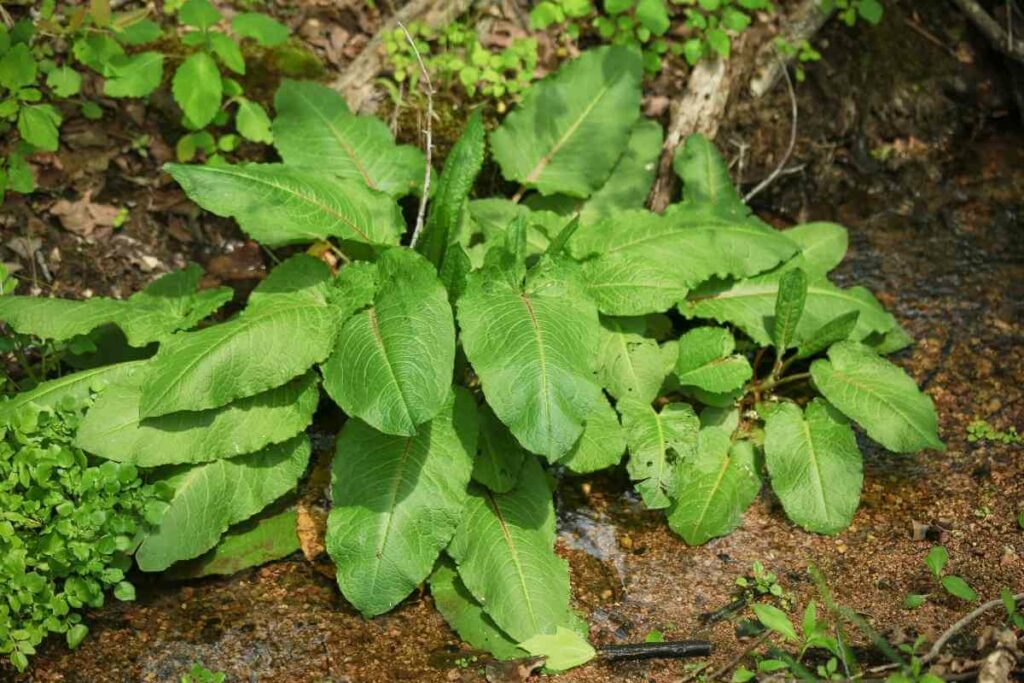

Distribution: Coastal areas of the UK, the Punjab, Australia, California, Washington DC.
Description
This relative of lettuces and the dandelion is fast-spreading, producing thick stems that can exceed 2 metres in height in a single growing season.
It has long leaves with a serrated edge and produces a dandelion-like flower. Wild lettuce has a potent sap that has pain-relieving properties.
Eradication strategies:
- Herbicidal control
- Hand pulling weeds
- Sustained animal grazing
7. Giant Hogweed
Also Known As: Heracleum Mantegazzianum, Giant Cow Parsley, Giant Cow Parsnip, Hogsbane
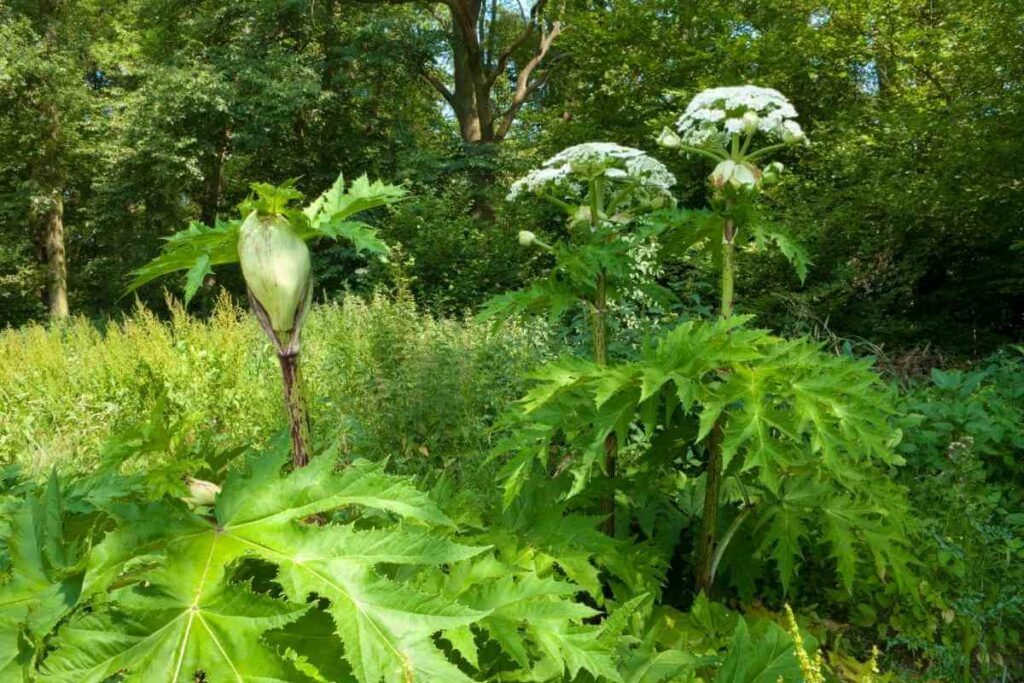

Distribution: Native to the Caucasus, spread to western Europe, the US and Canada.
Description
Giant hogweed is a noxious weed that can achieve heights of 5 metres or more.
It produces giant, deeply lobed leaves which grow off its thick green and purple stem.
At the top of the stem it has an inflorescence of green-white flowers arranged in an umbrella pattern.
The sap of this plant causes phototoxicity, leading to severe blistering on skin that has had contact with this plant.
It should not be handled without protective clothing, gloves and eye protection.
Eradication strategies:
- Herbicidal control
- Uprooting emerging plants
- Removal of flower spikes before they can produce seed
8. Creeping Thistle
Also Known As: Cirsium Arvense, Canada Thistle and Field Thistle
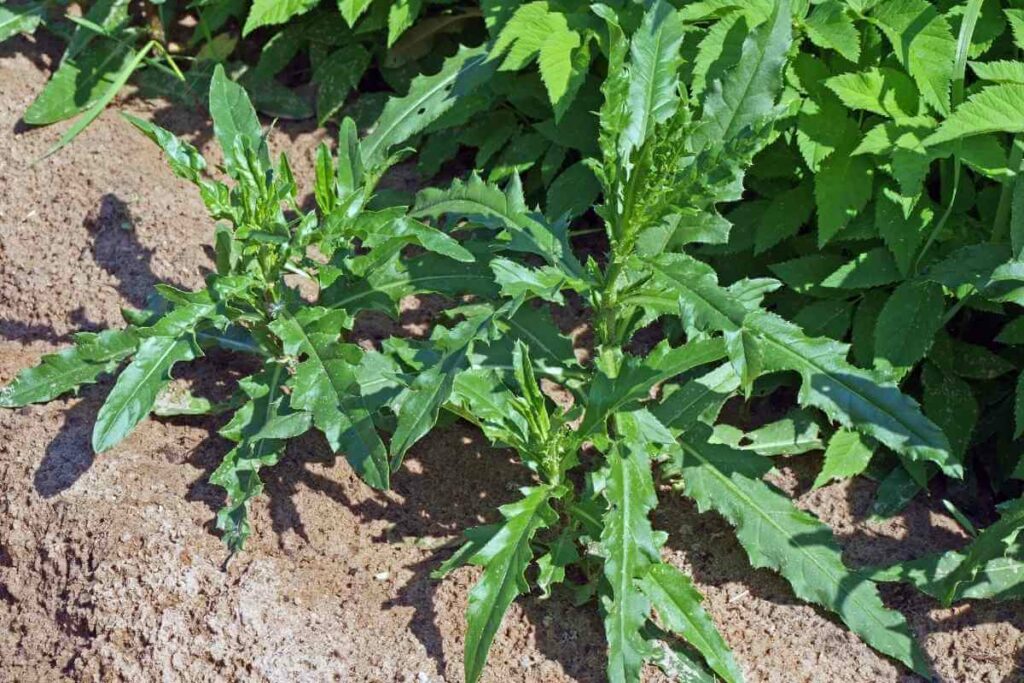

Distribution: Native to the Caucasus, spread to western Europe, the US and Canada.
Description
This herbaceous perennial can rapidly take over large areas of land by forming a network of clonal colonies with numerous erect flowering shoots of up to 1.5 metres in height.
This weed is incredibly invasive and adapts to and spreads through any environment that it encounters.
Its fast turnover means that it evolves quickly to establish itself and can evade chemical methods of control.
Eradication strategies:
- Weakening plants by repeatedly cutting down growth
- Repeatedly digging up
- Weedkillers
9. Himalayan Balsam
Also Known As: Impatiens Glandulifera, Indian Balsam, Policeman’s Helmet, Jumping Jack
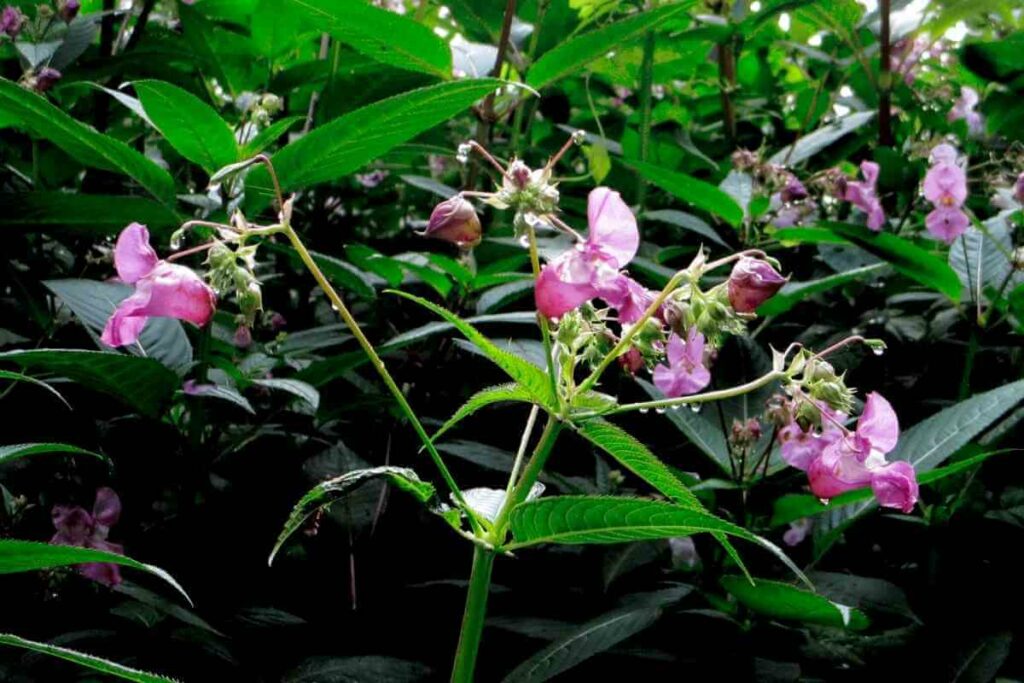

Distribution: Native to Nepal and India, spread to western Europe, the US and Canada.
Description
Himalayan Balm is a large annual with purple-pink helmet-like flowers that produce an edible nectar.
It was introduced to the UK in the late 1930s and has since become invasive.
Its annual growth achieves heights of up to 2 metres and it spreads prolifically through the exploding seed pods it produces.
Eradication strategies:
- pulling or cutting off the plants before they flower and set seed
- weed killer application including fatty acids and glyphosate treatments
10. Common Mullein
Also Known As: Verbascum Thapsus, Greater Mullein, Aaron’s Rod or The Great Mullein
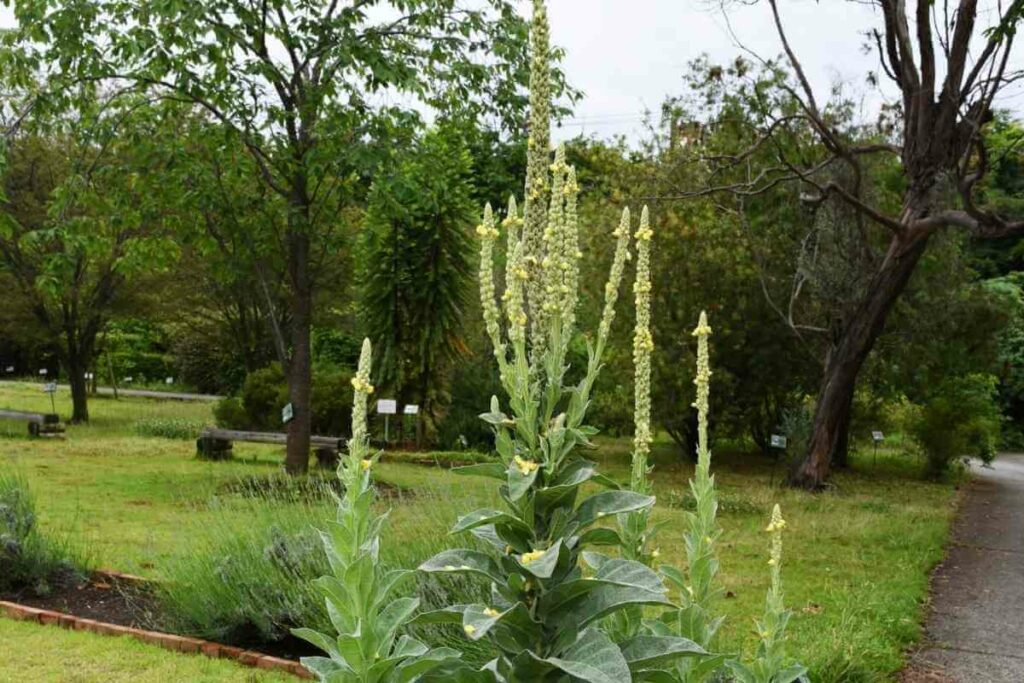

Distribution: Native to Europe, northern Africa and Asia, spread to the US, Canada and Australia.
Description
Common mullein produces tall (up to 3 metres), rod-like stems that bud and flower, but just like Aaron’s rod in the bible.
It produces rosettes of ovate leaves along its stem, followed by large light yellow flowers in its second year of growth.
Like many other weeds, it is aggressively invasive through the wide distribution of its seeds.
It is used in herbal medicine and in some cases is grown as an ornamental.
Eradication strategies:
- Biological control by the figwort weevil and caterpillars
- Manual weeding can be effective
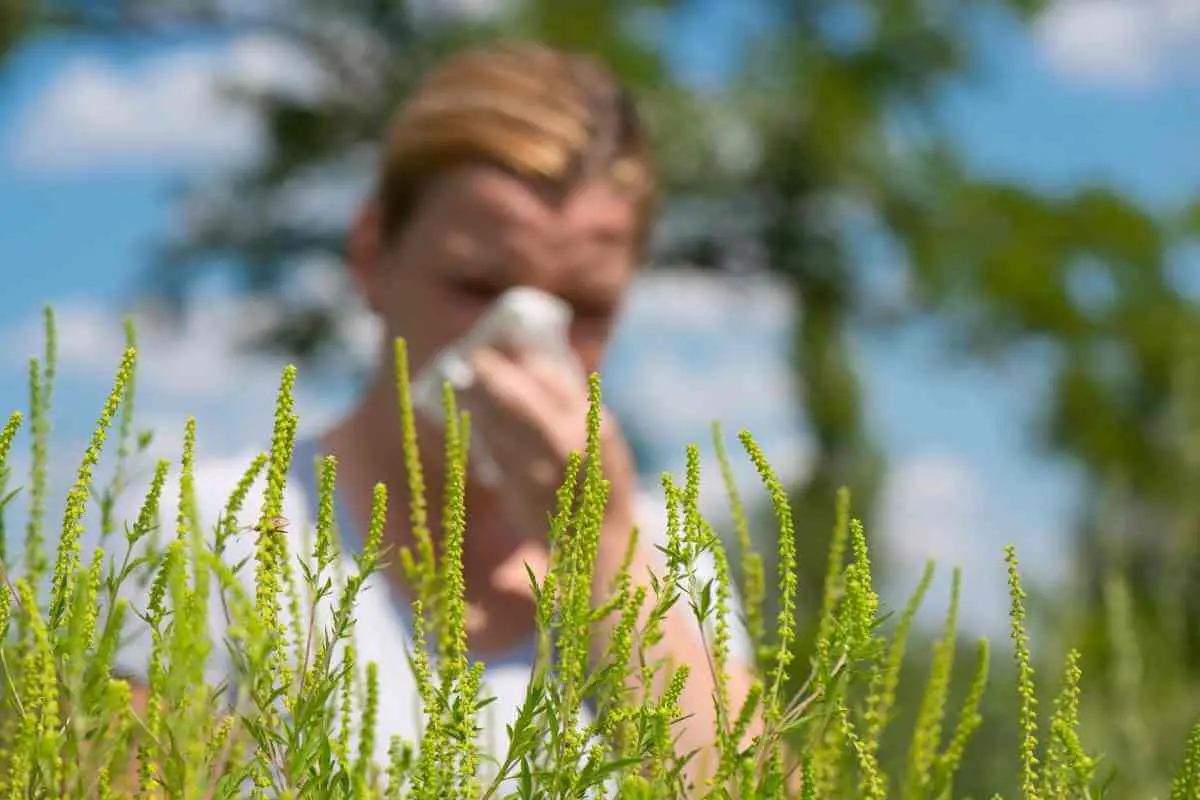
11. Giant Ragweed
Also Known As: Ambrosia Trifida
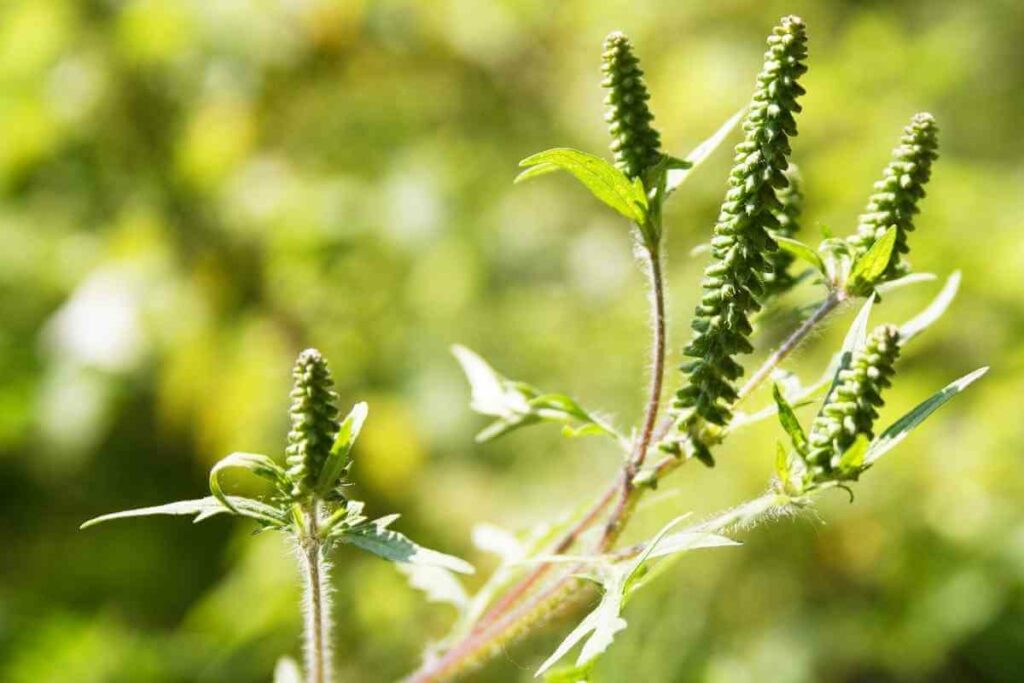

Distribution: Native to North America, spread to Europe and Asia.
Description
This invasive annual is a member of the sunflower family and produces tall tough stems that can exceed 4 metres in height in the right conditions.
Its leaves are also tough and it produces racemes of male and female flowers for efficient pollination.
The pollen produced by giant ragweed is highly allergenic and a significant contributor to hay fever cases.
It will spread and establish itself in areas that have fertile soils including agricultural land and flood plains.
Giant ragweed is highly adaptive with several strains being resistant to herbicides.
Eradication strategies:
- Stem boring
- Injection with glyphosate
Rounding Up
We hope you have found this rogues’ gallery of tall garden weeds helpful.
Controlling invasive species like these require persistence as even a small amount of root material that is left behind can give rise to a new plant.
For tall garden weeds, many gardeners reach for the glyphosate first, but many of these plants can be eradicated by manually uprooting them.
You will work up a sweat but clearing your land of these pesky weeds is well worth the effort!