Aquaponics systems have gained popularity over the past decade due to their ease of operation, sustainability, and the need to meet rising food demands.
It is the perfect balance between three symbiotic organisms: fish, plants, and nitrifying bacteria.
Whether you want to venture into aquaponics as a hobby or agribusiness, the first step is to design the system.
So how do you design an aquaponics system?
Before diving into the design details, we need to understand every aquaponic system’s essential components.
What Are the Essential Components That Make an Aquaponics System?
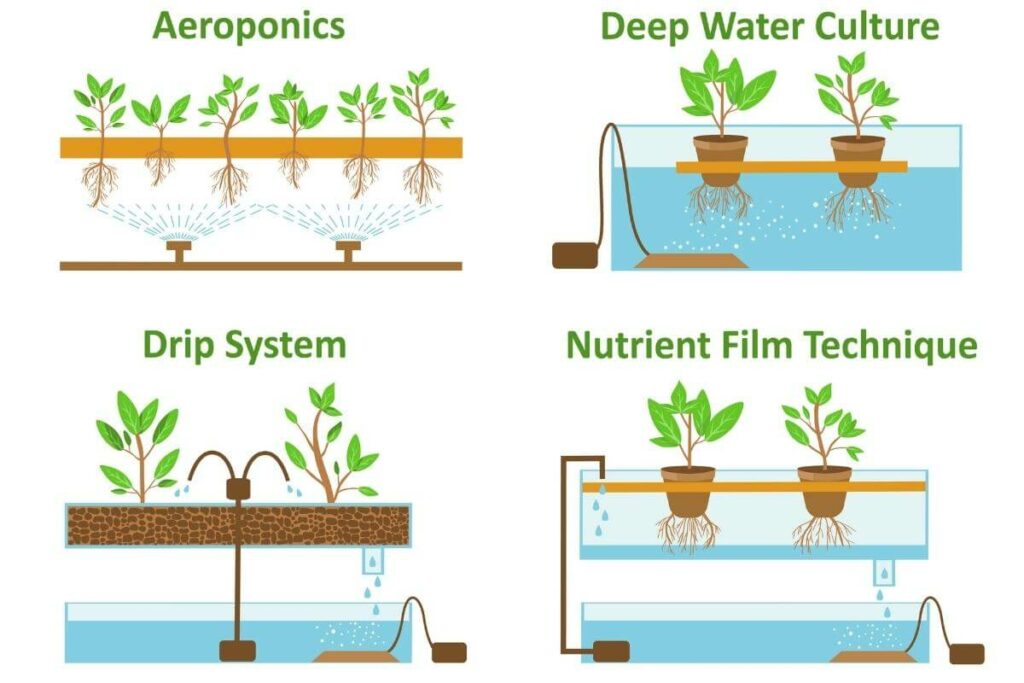
There are several aquaponics system designs that you can use to grow fish and vegetables at home or for commercial purposes.
These include:
- the media bed system
- nutrient film technique
- deep water culture system
Whichever design you choose, there are essential components that make the system complete, and a lack of any of these may cause challenges in the system.
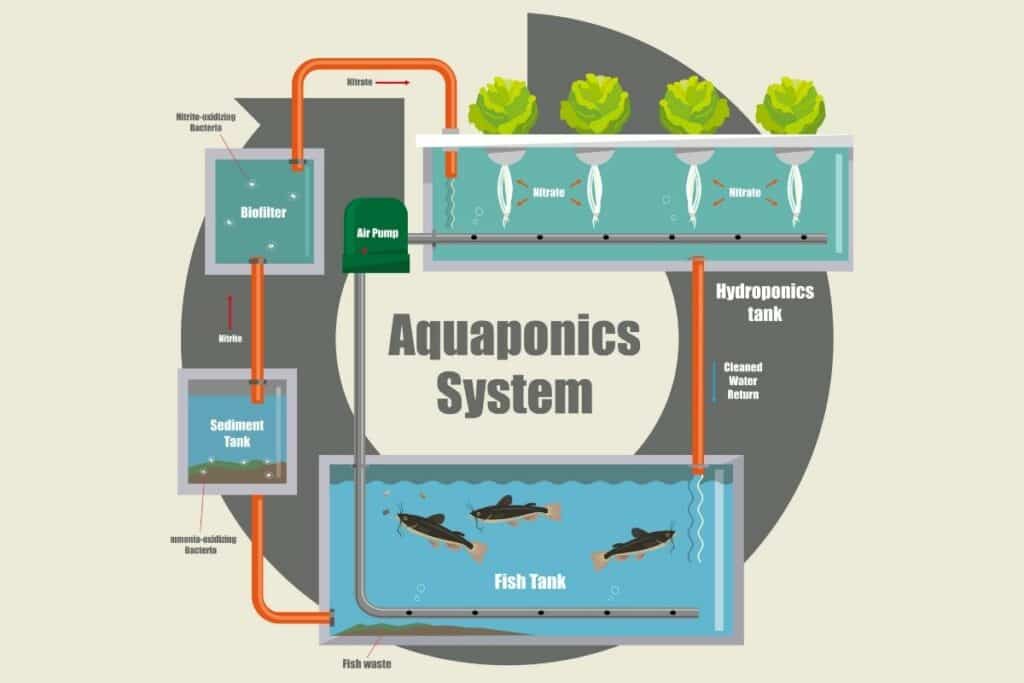
These components include the following:
- A fish tank
- Water pump
- Air pump
- Grow bed
- The sump tank (optional)
- Siphon
- Solid filter
- Bio filter
- Lighting
- Heating
- Fish
- Plants
- Nitrifying bacteria
- Water
- Security
- Growing trays
- Grow media
- Nets and cups
- Pipes and fittings
- Water quality test kit
- Monitoring device
- Fish food
Designing and setting up an aquaponic system doesn’t have to be expensive.
You can create do-it-yourself (DIY) components from plastic barrels, old bathtubs, and livestock water troughs in your home.
However, if you are not savvy with the technical stuff, you can buy ready-made components from an aquaponics essentials dealer near you.
What Conditions Have to Be Maintained to Design and Run an Aquaponics System Successfully?
Before we can talk about how to design your aquaponics system, there are growth conditions that cannot be compromised for the system to function.
A deviation or lack of these parameters may hurt the fish, causing stress or death.
The plants can also be affected, thus lowering your overall yields.
These conditions include:
- Oxygen levels
- Temperature
- Light
- PH.
Oxygen Levels
Fish need oxygen to survive.
A flawless aquaponics system should have adequate oxygen in the water to avoid stressing or killing the fish.
Deep water cultures may need seeding with air to introduce the much-needed oxygen and keep the cycle going.
This is done with an aerator, also known as an air pump.
Temperature
Water temperature is a critical determinant of the well-being of fish and bacteria in the aquaponics system.
Most nitrifying bacteria grow and work best between 26 and 36 degrees Celsius.
On the other hand, the fish are most productive between 20 and 30 degrees Celsius.
Finding a balance suitable for both species is vital to ensure maximum productivity.
Watch Out: Avoid placing the system under direct sunlight that may cause sharp fluctuations in temperatures.
Light
Plants need light for photosynthesis.
The fish also require a few hours of light for optimum growth, although excess light can stress them to the point of not eating their food.
Therefore, it is crucial to consider the lighting before designing your aquaponics.
You need to decide how you will control the light if you go for an outdoor system, and if you want an indoor one, invest in high-quality artificial light.
pH
The acidity or alkalinity of the water in an aquaponics system is critical to plants, fish, and bacteria.
Each of the three organisms requires an optimum pH, so you will need to control and maintain the water pH.
To keep the system suitable for all of them, maintain a pH between 6.8 and 7.2.
Regularly monitoring the water quality using a test kit is required to ensure all parameters are suitable for the three organisms.
Factors to Consider Before Designing an Aquaponics System
Designing aquaponics depends on whether you are doing it for fun or business.
If you mean business, you need to think of a cost-effective system to cater to your needs without breaking your bank account.

However, a small aquaponics system in your backyard does not require much investment.
The following factors should influence your aquaponics system design.
Your Gardening Goals
Suppose you are looking to put up an aquaponics system for fun or experimenting with a few fish and vegetables.
In that case, a simple and basic aquaponics design such as the media bed is ideal.
On the other hand, commercial projects require complex structures such as the Nutrient film’s vertical grow beds or floating deep water culture design beds.
Types of Plants You Plan to Grow
Small plants such as leafy vegetables, strawberries, etc., don’t need complex aquaponics systems and can grow on basic media beds and shallow nutrient film systems.
Technical Know-how
Some designs require constant monitoring and maintenance, but they yield excellent produce.
These include DWC and hybrid designs (two or more aquaponics designs, e.g., vertical grow beds combined with a raft system).
If you are a do-it-yourself enthusiast, such arrangements may be ideal for you.
However, if you don’t like handling technical issues, it’s best to go for simple designs that require minimal maintenance and monitoring.
Location
Where you want to place your aquaponics matters when designing an aquaponics system.
Be Creative: Choose a convenient and easily accessible location where you can monitor your fish, plants and do custom maintenance.
Space
The available space will determine how long or wide your system will be.
Basic media beds and NFT designs are ideal for limited spaces.
Go for the deep water culture type if you want to set up an extensive commercial aquaponics system.
How to Design an Aquaponics System
Designing an aquaponics system is not a complicated process with the right parts and materials.
Follow these steps to prepare an aquaponics of your choice.
Assemble the Fish Tank
You can buy a ready-made fish tank or make one yourself with old water barrels.
The size of your fish tank depends on the type and number of fish you want to rear.
As a rule of thumb, the fish tank should be twice the size of the grow bed. This ensures enough water in the tank, in the horse pipes, and in the grow bed doing circulation.
Add the pump, either a submersible or an inline pump, depending on the size of the system and design.
Install the correct arrangement:
- piping
- fittings
- siphon
- solid filters
- biofilters
Add chlorinated water and let it run for four to six weeks before adding the fish.
The quarantine period enables you to check the fish for infectious diseases and also gives the good bacteria time to grow in numbers.
Construct the Media Bed
Build the media bed above or by the side of the fish tank.
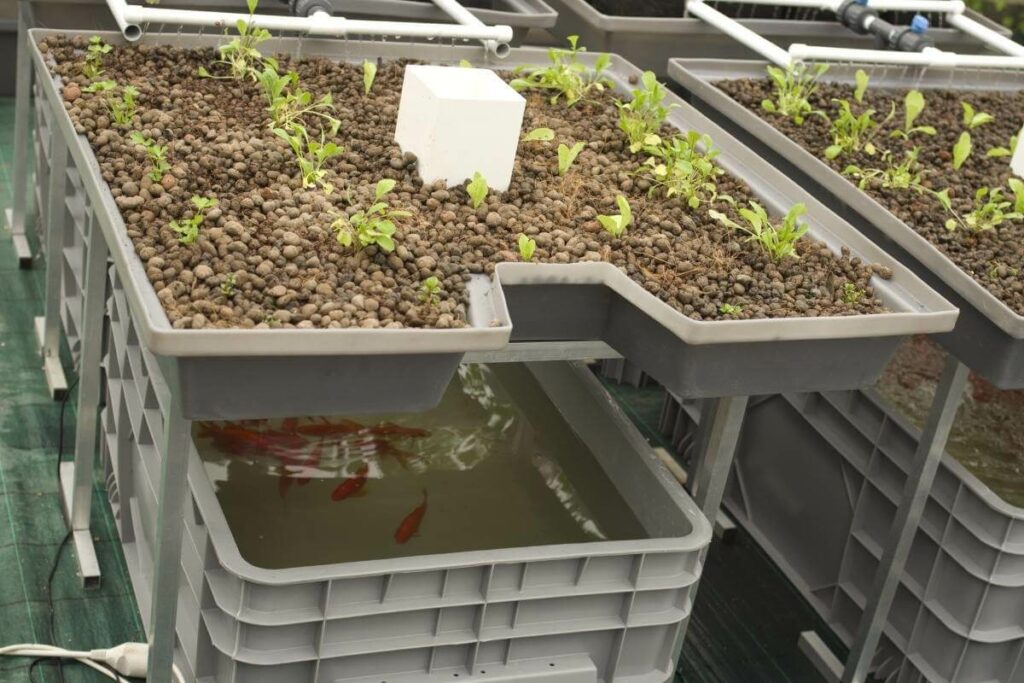

Prepare the growth media and arrange it appropriately in the media bed.
Growth media include baked clay, river rocks, gravel, etc.
Introduce the Fish to the Fish Tanks
After the cycling period elapses, add the fish.
Examples of common aquaponics fish are:
- tilapia
- barramundi
- goldfish
- catfish
- perch
- pacu
- koi
- carp
Add Your Plants
Introduce your preferred plants depending on the capacity and strength of the aquaponics system.
The best way to do this is to transfer pre-planted seedlings from a nursery to the media bed.
Monitor Your Aquaponics System
After introducing the plants, it’s time to keep a tab of the health of your fish and plants by maintaining optimum growth conditions such as temperature, pH, and light.
Conclusion
Designing an aquaponics system is the first step into growing fish and plants in a self-sustaining system.
Your design choice depends on your gardening goals, the type of plants you want to grow, space, your DIY spirit, and your system’s location.
To design a basic aquaponic system, assemble the fish tank, build the media bed, introduce the fish and finally add the plants.






